VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is a communication technology that logically divides a physical LAN into multiple broadcast domains. Each VLAN is a broadcast domain where hosts can communicate directly, while communication between different VLANs is restricted. As a result, broadcast messages are limited to a single VLAN.
Content
· Why VLANs are Needed · VLAN vs. Subnet · VLAN Tag and VLAN ID · Types of VLAN Interfaces and VLAN Tag Handling Mechanisms · Usage Scenarios of VLANs · Issues with VLANs in Cloud Environments
Why VLANs are Needed
Early Ethernet networks were data networking technologies based on CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection) that used shared communication mediums. When the number of hosts increased, it led to serious collisions, broadcast storms, significant performance degradation, and even network outages. Although interconnecting LANs using Layer 2 devices could resolve collision issues, it still failed to isolate broadcast messages and improve network quality. This led to the development of VLAN technology, which partitions a LAN into several logical VLANs; each VLAN represents a broadcast domain, enabling communication within the VLAN as if it were a LAN while preventing inter-VLAN communication and confining broadcast messages within a VLAN.
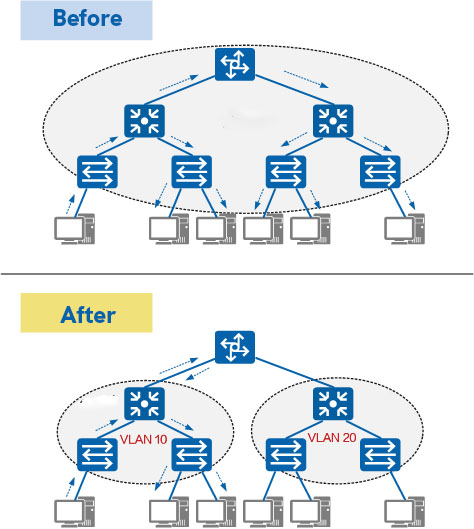
Illustration 1: The Role of VLANs
Thus, VLANs have the following advantages:
· Limiting Broadcast Domains: Broadcast domains are confined within a VLAN, conserving bandwidth and enhancing network processing capability. · Enhancing LAN Security: Messages from different VLANs are isolated during transmission, meaning users within one VLAN cannot directly communicate with users in another VLAN. · Increased Network Robustness: Faults are restricted to one VLAN, so issues within one VLAN do not affect the normal operation of other VLANs. · Flexible Virtual Workgroup Construction: VLANs can divide users into different workgroups, allowing members of the same workgroup to operate without being restricted to a particular physical area, making network construction and maintenance easier and more flexible.
VLAN vs. Subnet
By further subdividing the network part of IP addresses into several subnets, the low utilization rate of IP address space and the rigidity of two-level IP addresses can be addressed. Similar to VLANs, subnets can also isolate communication between hosts. Hosts belonging to different VLANs cannot communicate directly, just as hosts in different subnets cannot. However, there is no direct correspondence between the two.
| VLAN | Subnet |
|---|---|
| Difference | Used to divide Layer 2 networks. |
| After configuring VLAN interfaces, users in different VLANs can communicate only if routing is established. | |
| Up to 4094 VLANs can be defined; the number of devices within a VLAN is not limited. | |
| Relation | Within the same VLAN, one or more subnets can be defined. |
VLAN Tag and VLAN ID
To enable switches to distinguish messages from different VLANs, a field identifying VLAN information must be added to the messages. The IEEE 802.1Q protocol specifies that a 4-byte VLAN tag (known as VLAN Tag) be added to Ethernet data frames to identify VLAN information.
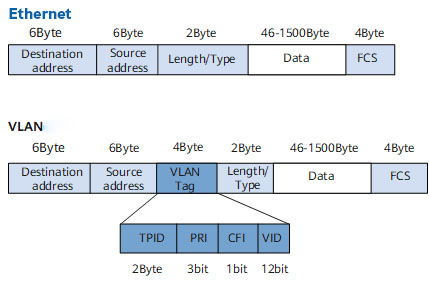
The VID field in the data frame identifies the VLAN to which the data frame belongs; the data frame can only be transmitted within its designated VLAN. The VID field represents the VLAN ID, which can range from 0 to 4095. Since 0 and 4095 are reserved by the protocol, the valid range for VLAN IDs is 1 to 4094. All data frames processed internally by the switch carry VLAN tags, while some devices (such as user hosts and servers) connected to the switch only send and receive traditional Ethernet frames without VLAN tags.
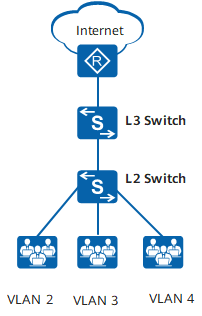
Therefore, to interact with these devices, switch interfaces must recognize traditional Ethernet frames and add or strip VLAN tags during transmission. The VLAN tag added corresponds to the interface’s default VLAN (Port Default VLAN ID, PVID).
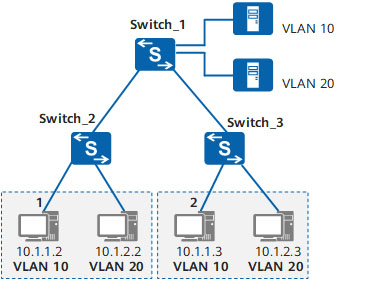
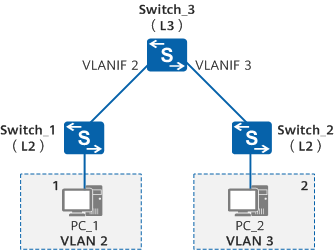

Types of VLAN Interfaces and VLAN Tag Handling Mechanisms
In current networks, users belonging to the same VLAN may be connected to different switches, and there can be multiple VLANs spanning across switches. If user intercommunication is necessary, the interfaces between switches must be able to recognize and send data frames from multiple VLANs simultaneously. Depending on the connected objects and how the frames are processed, there are various types of VLAN interfaces to accommodate different connections and networking.
Find ELV Cable Solution
Control Cables
For BMS, BUS, Industrial, Instrumentation Cable.
Click HereStructured Cabling System
Network&Data, Fiber-Optic Cable, Patch Cord, Modules, Faceplate
2024 Exhibitions & Events Review
Apr.16th-18th, 2024 Middle-East-Energy in DubaiSA. N32
Apr.16th-18th, 2024 Securika in MoscowHall.8 – D4041
May.9th, 2024 NEW PRODUCTS & TECHNOLOGIES LAUNCH EVENT in ShanghaiDouble Tree by HILTON – 2F – A Meeting Room
Oct.22nd-25th, 2024 SECURITY CHINA in BeijingE3.B29
Nov.19-20, 2024 CONNECTED WORLD KSA
Media Contact
Company Name: Shanghai AIPU WATON Electronic Industries Co., Ltd.
Email: Send Email
Country: China
Website: https://www.aipuwaton.com/
