In general, people who are obese or consume excessive alcohol are considered high-risk individuals for fatty liver. Excessive intake of fats will elevate blood lipid levels, and insufficient metabolic capacity of liver cells to process lipids, which can lead to the accumulation of fat in the liver and result in fatty liver. Alcohol consumption can also produce harmful substances during metabolism in the liver, exceeding its compensatory capacity, thereby damaging liver cells and causing alcoholic fatty liver.
Does this mean that individuals who are thin or do not drink alcohol are impossible to get fatty liver?
Even those who follow a vegetarian diet or have poor and unbalanced nutrition can potentially develop fatty liver. Thin individuals may accumulate fat in the liver due to their lower capacity for fat storage in the body. Additionally, a deficiency in protein, leading to a reduced synthesis of very low-density lipoproteins, weakens the liver’s ability to transport fat, resulting in the accumulation of fat in the liver.
This discovery is intriguing because, traditionally, the first recommendation for treating fatty liver was to control intake. However, there is now a more precise target: the liver cells. Improving the functionality of liver cells may have a positive effect on alleviating fatty liver, especially for those who do not respond well to dietary restrictions.
Existing treatment measures for fatty liver targeting liver cells include:
1. Dietary Adjustment:
Focus on reducing the burden on liver cells by advocating a high-protein, high-vitamin, low-sugar, and low-fat diet. This involves avoiding or minimizing the intake of animal fats, sweets (including sugary beverages), consuming vegetables, fruits, fiber-rich foods, as well as high-protein lean meat, river fish, and soy products. Snacking and late-night meals should be avoided.
2. Medication:
Medicine care often includes hepatoprotective, lipid-lowering drugs, and antioxidants. Examples include phospholipids, ursodeoxycholic acid, silymarin, inosine, coenzyme A, reduced glutathione, taurine, and whey acidic proteins. While these drugs are mature in their development, their effectiveness varies from person to person, and currently, there is no universally effective medication. However, they are often used as supplementary treatment options.
3. Nutritional Therapy Research:
Nutritional therapy is particularly popular in Europe, which focuses on the positive effects of nutrients on liver cell activity. The latest research indicates that nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, dietary fiber, and proteins can promote normal metabolism, prevent nutrient deficiencies, and facilitate the repairing and regeneration of liver cells. Examples include:
Vitamin E: Exhibits antioxidant activity, reducing liver compensation rates.
Vitamin D: Significantly metabolizes free fatty acids directed to the liver, inhibits fat deposition in liver cells, alleviates insulin resistance, and has a therapeutic effect on fatty liver.
Myo-inositol and Chiro-inositol: Lower and inhibit the increase in blood lipid levels caused by alcohol, inhibit serum AST activity, reduce liver lipid content, lower MDA content, effectively alleviate oxidative damage to the liver, eliminate free radicals in the liver, and protect liver cells.
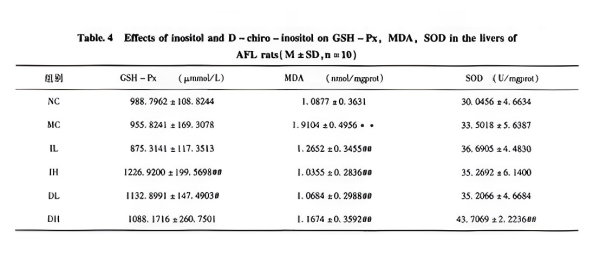
Especially in cases of fatty liver combined with lipid metabolism disorders, there is a certain correlation between blood lipids and the degree of fatty liver damage. Lowering blood lipids can to some extent improve hepatic cell fat degeneration, particularly in alcoholic fatty liver.
PQQ :Pyrroloquinoline Quinone and Quinoline Quinone Sodium Salt:
A new ingredient that has gained popularity in academic circles in recent years, contributing to the well-being of humanity. Through repeated scientific experiments, it has been proven to target liver cells, promote the generating of new mitochondria within cells, and exhibit a potent antioxidant effect, significantly reducing oxidative stress reaction in liver cells. It aids in eliminating free radicals within the liver, with an antioxidant efficacy 5000 times that of Vitamin C, achieving cellular-level liver repair.
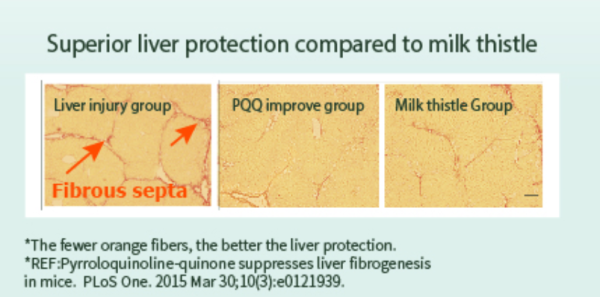
Transaminase and triglycerides are two prominent indicators of fatty liver, and PQQ’s performance in these aspects is unexpectedly outstanding, even surpassing traditional milk thistle.
“Oral intake of PQQ is beneficial in reducing transaminases and improving alcoholic fatty liver.”
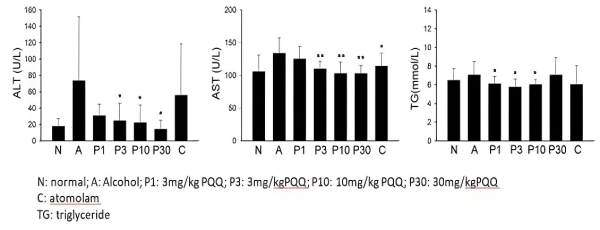
The daily oral intake of 10mg/kg of PQQ brings about changes in triglycerides:
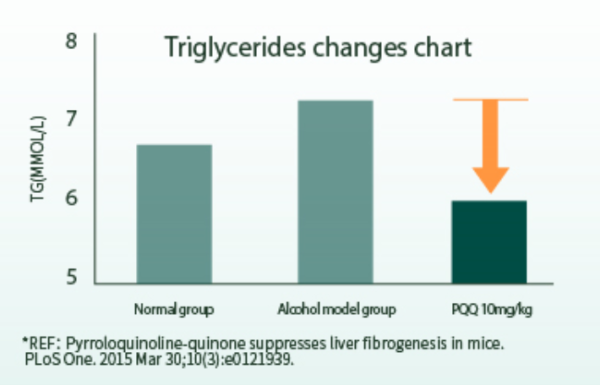
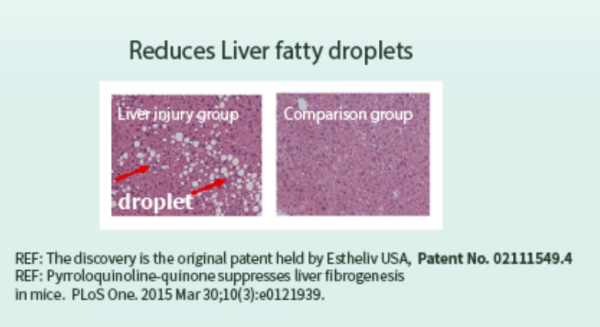
Furthermore, two additional indicators are associated with the protection against liver damage and a reduction in lipid droplets within liver cells. Two experiments from ESTHELIV, sourced directly from their website, have been discovered, and accompanying screenshots are provided.
In the course of research, the discovery was made that ESTHELIV has introduced a formula combining PQQ with inositol, referred to as “Liver Detox Capsules.” Notably, this brand holds a patent for inventions related to fatty liver and has received certification from the FDA. It suggests that there is something substantial in terms of liver protection within their offerings.

The dosage is also decent, with 100mg of inositol and 20mg of PQQ. This PQQ content is tenth as high as their experimental 10mg, but still within the safe dosage range. Moreover, they use 99.942% of a high-purity, highly stable PureQQ; since their patented PQQ component currently are highest purity and stability PQQ globally. This suggests that the user experience and effectiveness should be even better.
Given this formula, there is a perception that the ESTHELIV Liver Detox Capsules could potentially have a beneficial detoxification effect, as it has the potential to expedite alcohol metabolism while safeguarding liver cells. The intention is to experiment with it the next time alcohol is consumed.
The ESTHELIV Liver Detox Capsules can repair damaged liver cells, accelerate liver metabolism, combat oxidative stress on liver cells, protect liver cells, and help metabolize fats and emulsify cholesterol. This product specifically targets liver cells, making it suitable for those with fatty liver or anyone interested in liver protection.
https://www.zhihu.com/question/19924754/answer/2092919225
References:
Data sources:
Pyrroloquinoline-quinone suppresses liver fibrogenesis in mice. PLoS One. 2015 Mar 30;10(3):e0121939.
Research on the effects of inositol and D-chiro-inositol on alcoholic fatty liver in rats.
This discovery is held by the original research of the American company Estheliv, patent number: 02111549.4.
Media Contact
Company Name: ESTHELIV,INC
Contact Person: Becko
Email: Send Email
Country: United States
Website: www.estheliv.com
