With the development of the Internet, services such as online pictures, videos and streaming media have placed higher bandwidth requirements on wireless LAN technology. is also known as the “High Efficiency Wireless Standard”.

In fact, 802.11ax was designed to solve the problem of network capacity, which has become a major issue in dense environments such as airports, sporting events and campuses as public Wi-Fi has become more popular. So what are the specific technical breakthroughs of 11ax as a new generation of WiFi protocol?

1. wifi6 supports 2.4G and 5G
The 802.11ax protocol is based on two frequency bands, 2.4GHz and 5GHz. This dual band is not a different protocol for different frequency bands like ac dual band routers, but the ax protocol itself supports two frequency bands. This obviously caters to the current trend of IoT, smart home and other developments. For some smart home devices that do not need high bandwidth, you can use the 2.4GHz band to connect to ensure sufficient transmission distance, while for devices that need high-speed transmission, use the 5GHz band.

2. Support 1024-QAM, higher data capacity
In terms of modulation WiFi 5 is 256-QAM and WiFi-6 is 1024-QAM, the former supports a maximum of 4 data streams while the latter supports a maximum of 8. Therefore, WiFi 5 can achieve a theoretical throughput of 3.5Gbps, while WiFi 6 can achieve an amazing 9.6Gbps.

3. Support for full version of MU-MIMO
MIMO means Multiple Input Multiple Output technology, which refers to the use of multiple transmitting and receiving antennas at the transmitter and receiver ends respectively, so that signals can be transmitted and received through multiple antennas at the transmitter and receiver ends to achieve higher user rates at a smaller cost, thus improving communication quality. In fact, MIMO technology was introduced by IEEE in the 802.11n protocol era, and MU-MIMO technology can be understood as an upgraded or multi-user version of it.
In layman’s terms, the previous MIMO on 802.11n can only be described as SU-MIMO, where the traditional SU-MIMO router signals are presented in a circle, communicating individually with Internet access devices in order of proximity. When too many devices are connected, there will be devices waiting for communication; if you have 100MHz of bandwidth, according to the principle of “only one can serve at a time”, if there are three devices connected to the network at the same time, each device can only get about 33.3MHz of bandwidth, and the other 66.6MHz is idle. The other 66.6MHz is unused. This means that the more devices connected to the same Wi-Fi area, the smaller the bandwidth is averaged out, the more resources are wasted and the slower the network speed.
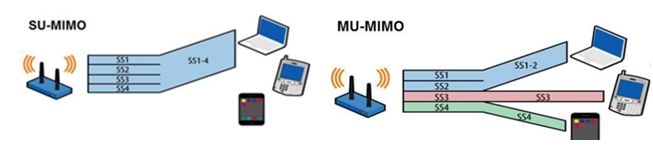
The MU-MIMO router is different, as the MU-MIMO routing signal is divided into three parts in the time domain, frequency domain and airspace domain, as if three different signals are emitted at the same time, and can work with three devices at the same time; especially worth mentioning is that, as the three signals do not interfere with each other, so the bandwidth resources received by each device is not compromised, and the resources are maximised. From the router’s perspective, the data transmission rate is increased by a factor of three, improving the utilisation of network resources and thus ensuring uninterrupted Wi-Fi connectivity.
4. OFDMA technology
OFDM, or Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing, is a multi-carrier transmission scheme developed from multi-carrier modulation with low implementation complexity and the widest range of applications. To illustrate with a simple example: suppose we now have many cars to go from A to B. Before the use of OFDM technology, the road is a road, all the cars drive around and rampage, as a result, no one can be faster. Now with OFDM technology, a big road is divided into many lanes and everyone drives according to the lane, which can increase the speed and reduce the interference between cars. At the same time, when there are more cars in this lane, they are evened out a little to that lane with fewer cars, which is much easier to manage.

OFDMA technology evolved from OFDM by adding multi-access (i.e. multi-user) technology to it.
The OFDM solution is to send a truck once for each customer. Regardless of the amount of cargo, one single trip is sent, which inevitably results in an empty van. The OFDMA solution, on the other hand, will ship multiple orders together, allowing the trucks to hit the road as fully loaded as possible, making transport much more efficient.
Not only that, but the effects of OFDMA and MU-MIMO can be superimposed under WiFi6. The two present a complementary relationship, with OFDMA being suitable for parallel transmission of small packets to improve channel utilisation and transmission efficiency. MU-MIMO, on the other hand, is suitable for the parallel transmission of large packets, increasing the effective bandwidth of a single user and also reducing latency.
Comparison of 5G and WIFI6
1. Application scenarios:
5G LTE routers are used in a wide range of applications, such as
1. Transportation: 5G LTE routers can be used to provide high-speed internet connections to vehicles such as buses, trains and trucks. They enable passengers to access the Internet and stream video while on the go.
2. Energy: 5G LTE routers can be used to provide high-speed Internet connections to remote energy sites such as wind farms and oil rigs. They enable employees to access real-time data and communicate with colleagues.
3. Public safety: 5G LTE routers can be used to provide high-speed Internet connectivity for emergency responders such as police and firefighters. They enable responders to access critical information and communicate with colleagues in emergency situations.
4. Retail: 5G LTE routers can be used to provide high-speed Internet connectivity to retail shops, enabling them to offer a personalised shopping experience and real-time inventory management.
Whereas WiFi6 is primarily focused on indoor short-range coverage, Wi-Fi6 is a great choice for corporate offices. Providing more options for businesses to be smarter. In addition, from the perspective of home users’ usage, only wifi6 can bring out the maximum effectiveness of 5G.
2. From a technical level
The ideal rate of wifi6 is 9.6Gbps, while the ideal rate of 5G is 10Gbps, not much difference between the two ideal rates.
Coverage, coverage is related to the transmitting strength, Wi-Fi6 APs cover about 500 to 1000 square meters; an outdoor 5G base station can transmit up to 60W, its coverage is kilometre level. In terms of coverage area, 5G is superior to wifi6.
Indoor single user experience: Wi-Fi6 APs can be up to 8T8R, with an actual rate of at least 3Gbps-4Gbps. a typical indoor 5G small base station antenna is typically 4T4R, with an actual rate of 1.5Gbps-2Gbps. so, single device performance Wi-Fi6 will outperform 5G.
3. Construction costs:
5G networks need to be verified by close planning and simulation due to the easy fading of signals. In addition, the characteristics of 5G bands and wavelengths require 5G base stations to be more dense, resulting in high input base station costs.
In contrast, the upgrade of wifi6 only requires an upgrade of the main chip, and the deployment can be achieved by simply purchasing a whole Wi-Fi6 AP once the fibre is in the home or into the enterprise.
5G and Wifi6 each have their own strengths and weaknesses. 5G is an operator network with authorised frequency bands, while WiFi is a non-authorised band, similar to a private network, and even if 5G gets a non-authorised band, it is difficult to bring down the cost of access points due to the inconvenience of networking and the short term, so WiFi 6 becomes a good complement to this piece of indoor IoT.
For example, if we compare communication technology to transportation, 5G is like an aeroplane that can quickly transport express mail from one city to another, but it can’t help you pick up takeaways within 1 km, and it’s better to use the most advanced electric car to pick up takeaways.
Welcome to visit ZBT website to get more information about wireless routers:
https://www.4gltewifirouter.com/
Media Contact
Company Name: Shenzhen Zhitotong Electronics Co.LTD
Email: Send Email
Country: China
Website: https://www.4gltewifirouter.com/
